Key Takeaways:
- Plyometric exercises are designed to increase explosive power and athletic performance through rapid, forceful movements.
- Proper form and progression are crucial in plyometric training to prevent injury and maximize benefits.
- Plyometric training can be integrated into a variety of fitness routines to enhance strength, speed, and agility.
Plyometrics Explained
Plyometrics, often referred to as jump training or plyos, are exercises designed to produce fast, powerful movements. They are intended to increase both speed and power, which are essential components of athletic performance. This training focuses on learning to move from a muscle extension to a contraction in a rapid or "explosive" manner, such as in specialized repeated jumping. Plyometrics are primarily used by athletes, especially martial artists, sprinters, and high jumpers, to improve performance, and are a key component in many other sports' conditioning programs.
The term "plyometrics" was coined by Fred Wilt after watching Soviet athletes prepare for their events by jumping up and down, hopping, and skipping before track and field competitions. The word is derived from the Greek words "pleythyein" (to increase) and "metric" (to measure). Plyometric training can be a critical component of a strength and conditioning program, with a wide range of exercises that can be tailored to benefit virtually any athlete.
Understanding the Science of Plyometric Training
Understanding the science behind plyometrics can greatly enhance an athlete's approach to training. The stretch-shortening cycle (SSC) is a fundamental concept in plyometric exercises, where muscles undergo a rapid stretch followed by an immediate shortening action. This cycle exploits the elastic properties of muscles and connective tissues, leading to more powerful movements. For instance, during plyometric push-ups, the chest and arm muscles stretch as the body lowers toward the ground, then contract rapidly to push the body upwards.
By training the SSC through various plyometric exercises, athletes can improve their body's ability to generate force quickly. This is particularly beneficial in sports where explosive actions are frequently required, such as basketball or volleyball. Regularly practicing plyometrics can enhance the efficiency of the SSC, leading to gains in speed, power, and overall athletic performance.
The Role of Plyometrics in Athletic Performance
Athletes across various sports utilize plyometric training to enhance their performance. The explosive power developed through plyometrics is essential for sports that require sudden bursts of speed or force, such as basketball, soccer, and track and field. By improving the efficiency and speed of the SSC, athletes can jump higher, run faster, and react more quickly during competition.

Incorporating Plyometrics into Your Training Routine
When integrating plyometric exercises into a training routine, it's important to start with basic movements and gradually progress to more advanced drills. Beginners should focus on mastering the technique of each exercise before increasing the intensity or complexity. Plyometric training should also be balanced with other forms of exercise to ensure overall muscular development and injury prevention.
Safety Considerations and Injury Prevention
Safety is paramount when performing plyometric exercises. Due to the high-impact nature of these movements, there is an increased risk of injury if they are performed incorrectly or without proper progression. Athletes should ensure they have a solid foundation of strength and flexibility before beginning plyometric training and should always prioritize proper form to minimize the risk of injury.
Plyometric Exercises for the Lower Body
Lower-body plyometric exercises are designed to enhance the explosive power of the legs and hips. Some popular lower-body plyometrics include squat jumps, tuck jumps, and box jumps. These exercises target the major muscle groups of the lower body, including the quadriceps, hamstrings, glutes, and calves, and are essential for sports that require jumping or rapid changes in direction.
Upper Body Plyometrics for Strength and Power
While plyometrics are often associated with lower-body training, there are also upper-body plyometric exercises that can significantly improve upper-body power. Exercises like plyometric push-ups and medicine ball throws are designed to increase the explosive strength of the chest, shoulders, and arms. These movements are particularly beneficial for athletes involved in throwing sports or combat sports where upper body power is crucial.
Drills for Improved Speed and Agility
Plyometric drills can also be used to improve an athlete's speed and agility. Lateral jumps, single-leg hops, and agility ladders are examples of plyometric exercises that enhance an athlete's ability to move quickly and change direction efficiently. These drills are often incorporated into the conditioning programs of athletes who participate in sports that require high levels of footwork and coordination.
Training for Enhanced Coordination and Balance
Plyometric training isn't just about developing power; it's also a fantastic way to enhance coordination and balance. When you perform a plyometric exercise like a tuck jump or lateral jump, you're not only working on force production but also on the specific movement pattern that requires precise motor control. This is because plyometrics demand that the body's ability to stabilize during dynamic movements is constantly challenged. As you leap from a squat position into a vertical jump, your muscles must work harmoniously to maintain your balance upon landing.
Moreover, the balance benefits of plyometrics can translate into better performance in various sports. For instance, a basketball player who incorporates plyo moves such as single-leg jumps and box jumps into their exercise program may notice an improvement in their ability to maintain control during quick directional changes on the court. Similarly, a soccer player might find that plyometrics help in mastering the art of maintaining feet shoulder-width apart while executing explosive running or changing pace during the game. The key is the integration of these exercises into a well-rounded training regimen that prioritizes both the concentric phase of muscle contractions and the stabilization required upon foot contacts.

Training Adaptations and Long-Term Benefits
Plyometrics training is not just about the immediate gains in power and speed; it's also about the long-term adaptations your body undergoes. When you engage in exercises like jump squats or box jumps, you're not only working on your muscle contraction speed but also enhancing your body's ability to store and release energy efficiently. Over time, this can lead to significant improvements in overall athletic performance, as your muscles become more adept at handling high-intensity activities.
Moreover, plyometric programs are designed to progressively challenge your neuromuscular system, which can lead to better coordination and reaction times. Whether you're in a standing position ready to leap or preparing for a squat jump, the repeated explosive movements train your body to respond more quickly and powerfully. This is particularly beneficial for athletes who need to perform under pressure and can make the difference between a good performance and a great one.
Plyometric Progressions: From Beginner to Advanced
Plyometrics can be intimidating for beginners, but with the right progressions, anyone can harness the benefits of these dynamic exercises. Starting with basic movements like the jump squat, where your feet are shoulder-width apart, can set the foundation for more complex plyometric exercises. Beginners should focus on mastering the technique of these simpler exercises, ensuring they can perform them with proper form and without undue strain.
As individuals become more comfortable with the basics, they can gradually increase the intensity of their workouts. This might include transitioning from two-legged exercises to single-leg jumps, which require more balance and strength. It's crucial to listen to your body's ability to adapt to these exercises and to avoid overtraining. By progressively challenging the muscles, athletes can continue to improve their explosive power and athletic performance.
Plyometric Training and Body Weight Mastery
Plyometrics, often referred to as "jump training," primarily uses body weight to enhance muscular power. This exercise capitalizes on the stretch-shortening cycle of the muscles, which is pivotal in explosive movements. When engaging in plyometric training, athletes often start with their feet shoulder-width apart to maintain balance and ensure proper alignment. This stance is the foundation for many plyometric exercises, as it allows for a safe and effective launch and landing, minimizing the risk of injury and maximizing the potential for power development.
Body weight exercises like box jumps and single-leg jumps are staples in plyometric training because they require no equipment and can be performed almost anywhere. For instance, a box jump begins with an athlete in a semi-squat position, feet shoulder-width apart, and then propelling themselves onto a raised platform. This movement not only builds power but also improves the body's ability to absorb and redirect force, which is essential for many athletic activities. By mastering body weight control through plyometrics, athletes can significantly enhance their performance across various sports.
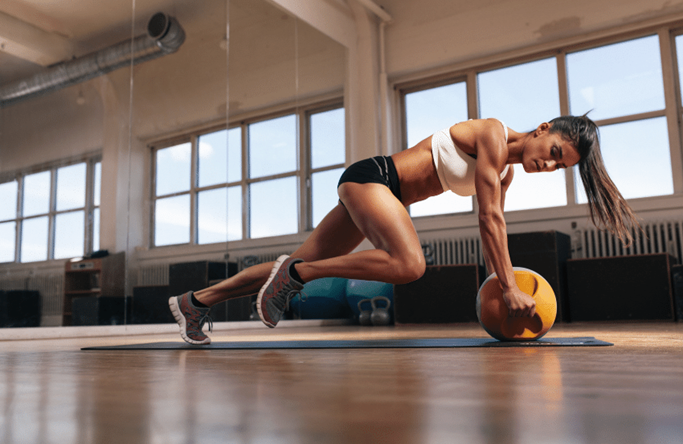

Training for Core Stability and Power
Plyometrics isn't just about the limbs; it's also crucial for developing a strong, stable core, which is essential for almost every athletic movement. When your feet are shoulder-width apart and you're exploding upwards in a jump, it's your core that maintains your balance and channels the power from your lower body to your upper body. A strong core can significantly enhance your body's ability to transfer force efficiently, which is vital for sports that require full-body power.
To specifically target the core, athletes can incorporate plyometric exercises like medicine ball throws and rotational tosses. These movements not only engage the core muscles but also mimic the explosive actions found in various sports, leading to improved performance. By integrating these core-focused plyometrics into a training routine, athletes can develop a powerhouse center that supports enhanced athletic ability across the board.
Training for Dynamic Footwork and Stability
Plyometric training isn't just about jumping higher or running faster; it's also about gaining dynamic footwork and stability. When athletes perform exercises with their feet shoulder-width apart, they're not only working on power but also on the balance and coordination required for quick, agile movements. This stance, often the starting position for many plyometric drills, provides a stable base that allows for explosive power to be generated from the lower body. It's a fundamental aspect that contributes to an athlete's ability to change direction swiftly and efficiently on the field or court.
Moreover, dynamic footwork is crucial in sports that demand sudden stops and starts or side-to-side movements. Plyometric training can enhance an athlete's ability to maintain control and balance when performing these complex maneuvers. By incorporating drills that mimic the specific footwork patterns of their sport, athletes can improve their neuromuscular responsiveness. This leads to better performance during competition, as their feet and ankles become adept at absorbing and redirecting forces quickly and safely.
Enhancing Upper Body Explosiveness with Plyometrics
While plyometrics is often associated with lower-body exercises, upper-body plyometrics can be equally beneficial in developing strength and power. Push-ups, for example, can be transformed into a plyometric workout by adding an explosive element. Instead of a traditional push-up, athletes can push forcefully off the ground to lift their hands, clapping in mid-air before landing. This explosive push-up variation not only targets the chest, shoulders, and triceps but also trains the body's ability to generate force rapidly.
Incorporating plyometric exercises for the upper body, such as medicine ball throws or plyometric push-ups, can significantly contribute to an athlete's overall explosive power. These movements require the muscles to contract quickly and forcefully, leading to improvements in upper body strength and power. By learning to effectively lean forward and engage the core during these exercises, athletes can enhance their performance in sports that require upper body explosiveness, such as boxing, swimming, or volleyball. Plyometric training for the upper body is an essential component for athletes looking to achieve a well-rounded and powerful physique.
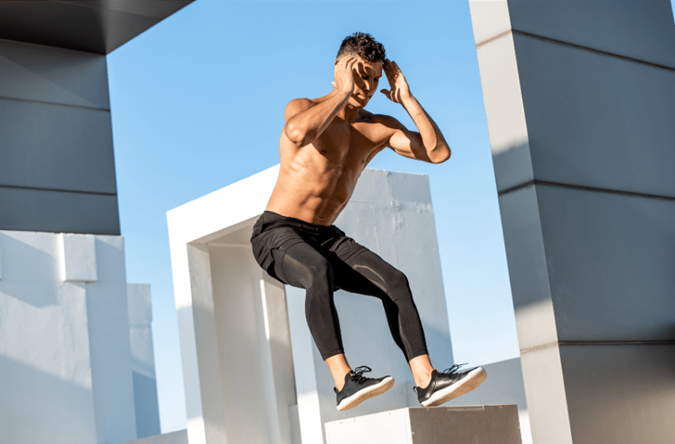

Plyometrics and Full-Body Engagement
While plyometrics are often associated with lower-body exercises like box jumps and jump squats, they can also be a powerful tool for full-body conditioning. For instance, plyometric push-ups are an excellent way to incorporate upper-body explosiveness into a routine. Starting in a traditional push-up position, the athlete explosively pushes up from the ground, allowing the hands to lift off the surface, before landing softly and with control.
Many exercises within plyometric training require a combination of upper and lower body coordination, which can significantly enhance an athlete's overall power. For example, a burpee with a tuck jump combines a push-up with a high-intensity jump squat, engaging the core, chest, and leg muscles simultaneously. This type of full-body plyometric exercise not only improves power but also increases the body's ability to work as a cohesive unit, which is essential for athletic performance.
Customizing Plyometrics
Plyometrics can be tailored to fit the needs of a wide range of individuals, from beginners to seasoned athletes. A personal trainer can be invaluable in helping to adjust the intensity and complexity of the exercises. For instance, someone new to plyometrics might start with basic squat jumps, keeping their feet shoulder-width apart and focusing on proper form, such as maintaining feet flat on the ground before takeoff and using an arm swing to gain momentum.
As individuals progress, more challenging variations can be introduced, such as single-leg jumps or incorporating strength exercises like push-ups into the plyometric routine. The key is to begin with a solid foundation in the starting position and then build up the complexity of the movements as the individual's strength and confidence grow. This personalized approach ensures that plyometrics training remains both safe and effective, allowing each person to maximize their athletic potential.
Designing a Plyometric Program for Optimal Results
Creating an effective plyometric program requires careful consideration of the athlete's current fitness level, goals, and sport-specific demands. A well-designed plyometric program will include a variety of exercises that target different muscle groups and movement patterns, with appropriate rest intervals to allow for recovery. It's also important to include a proper warm-up and cool-down to prepare the body for the intense demands of plyometric training.
The Importance of Progression and Overload in Plyometrics
Progression and overload are key principles in any training program, including plyometrics. As athletes adapt to the demands of plyometric exercises, it's important to gradually increase the intensity, volume, or complexity of the drills to continue challenging the muscles and making gains in power and performance. This can be achieved by adding weight, increasing the height of jumps, or incorporating more dynamic movements.
Combining Plyometrics with Other Training Modalities
For a comprehensive approach to fitness and performance, plyometrics should be combined with other training modalities such as strength training, cardiovascular conditioning, and flexibility exercises. This holistic approach ensures that athletes develop a well-rounded set of physical attributes and reduces the risk of overtraining any specific muscle group.
Measuring the Effectiveness of Plyometric Training
To gauge the effectiveness of a plyometric program, athletes can track various performance metrics such as jump height, running speed, and overall power output. Regular testing and monitoring can help identify areas of improvement and guide adjustments to the training regimen. It's also important to consider subjective measures such as how the athlete feels during and after workouts.
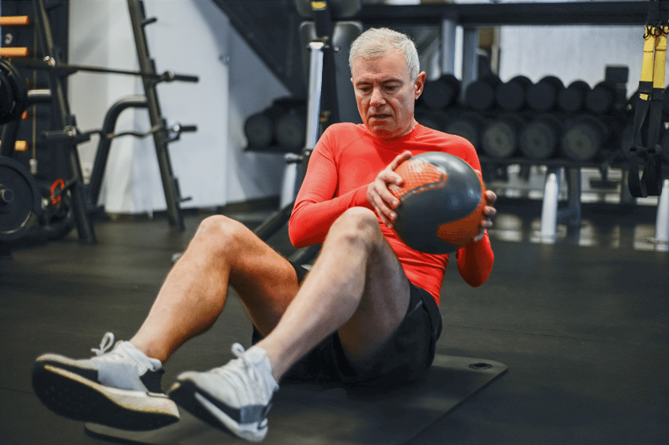

Plyometric Training for Different Age Groups and Skill Levels
Plyometric training can be adapted for individuals of different ages and skill levels. While the intensity and complexity of exercises may vary, the benefits of plyometrics can be experienced by youth athletes, recreational exercisers, and elite competitors alike. It's crucial to tailor the exercises to the individual's capabilities and to ensure that they are performed with proper technique to prevent injury.
The Future of Plyometrics in Sports Training
As research continues to uncover the benefits of plyometric training, its application in sports training is likely to expand. Innovations in technology and training methods may lead to new plyometric exercises and programs that are even more effective at enhancing athletic performance. Coaches and athletes should stay informed about the latest developments in the field to maintain a competitive edge.

Plyometric FAQs
What are plyometric exercises?
Plyometric exercises are dynamic movements that involve rapid stretching and contracting of muscles to increase muscle power. They typically include jumps, hops, and bounds that require the muscles to exert maximum force in short intervals of time.
What is an example of plyometrics?
Box jumps are a classic plyometric example. Leap onto a sturdy box, engaging muscles explosively. This exercise builds lower body power, boosts agility, and adds an exhilarating edge to your workout.
How often should I do plyometric training?
The frequency of plyometric training can vary based on your overall fitness routine and goals. Generally, it's recommended to perform plyometric exercises 1-3 times per week, allowing for adequate rest and recovery between sessions.
Can plyometrics help with weight loss?
Yes, plyometric exercises can contribute to weight loss as they are high-intensity movements that burn a significant number of calories. However, for optimal weight loss results, plyometrics should be combined with a balanced diet and other forms of exercise.
What are the disadvantages of plyometric training?
Plyometric training, while effective, may pose injury risks if not done with proper form or by those with existing joint issues. It's crucial to start gradually, ensuring a balanced approach to avoid overuse injuries.
How do I start plyometrics?
Start plyometrics gradually. Begin with basic moves like squat jumps, focusing on form. Gradually increase intensity and complexity. Prioritize proper warm-up to prevent injuries. Consult a fitness professional for personalized guidance based on your fitness level.
Do plyometrics count as cardio?
Yes, plyometrics, with its explosive and dynamic moves, elevates the heart rate, making it an effective cardiovascular workout. It enhances endurance, burns calories, and contributes to overall cardiovascular fitness. Add plyometrics to your routine for a cardio boost with a side of power.

May we say in conclusion...
Plyometric training is a dynamic and effective way to enhance explosive power and athletic performance. By incorporating plyometric exercises into a well-rounded training program, athletes can improve their speed, strength, and agility, which are essential for success in a wide range of sports.
It's important to approach plyometrics with a focus on proper form, progression, and safety to maximize benefits and minimize the risk of injury. With the right guidance and dedication, plyometric training can be a game-changer for athletes looking to take their performance to the next level. 👇